

We know that supporting children’s social and emotional development is key to school readiness and overall healthy growth and development. This lesson will introduce several evidence-based practices and resources taken from the Center on the Social and Emotional Foundations for Early Learning (CSEFEL).
Information shared are applicable for teaching and caring for infants, toddlers, and preschool age children. If you currently care for only one of these age groups you will benefit from learning about the entire birth to five developmental spectrum. You will then understand what the children in your care have already achieved and what lies ahead.
In this lesson you will read information based on current research. You will view video scenarios from real practitioners in childcare. You will also complete activities and handouts throughout the lesson that help you apply the information to your care of infants. Be sure to take notes as you work on this lesson.
As you work through this lesson there are handouts to download and print. Some handouts are writable PDF’s where responses or information can be typed and then printed. You can choose to print the blank handout and complete by hand. The handouts contain activities, additional ways to enhance learning, information to share with colleagues or parents, and strategies to apply what you learned to your daily care of infants.
We know that supporting children’s social and emotional development is key to school readiness and overall healthy growth and development. This lesson will introduce several evidence-based practices and resources taken from the Center on the Social and Emotional Foundations for Early Learning (CSEFEL).
Information shared are applicable for teaching and caring for infants, toddlers, and preschool age children. If you currently care for only one of these age groups you will benefit from learning about the entire birth to five developmental spectrum. You will then understand what your children have already achieved and what lies ahead.
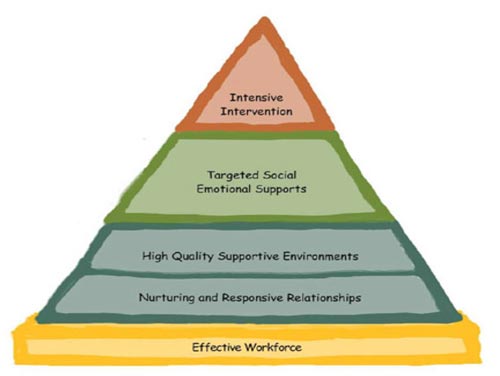
While many approaches and methods have been used in various early childhood settings to address young children, the "Pyramid Model" is an evidence-based model for preventing challenging behaviors in young children and supporting social competency. The model approaches challenging behaviors of young children through a comprehensive and systematic process.
The pyramid framework includes the following strata, beginning at the base with effective workforce and moving upward:
The pyramid is inclusive of early childhood positive behavioral intervention and support strategies.
Early childhood professionals and parents are confronted with difficult situations when responding to children's challenging behaviors. Through implementing the strategies of the Pyramid Model, preventative measures are emphasized. The pyramid emphasizes the need to view children's behavior challenges through building relationships, arranging environments and teaching social skills. Responses to children's behaviors are planned and intentional.
The strategies of the Pyramid Model are for all early childhood care and education programs.
The information presented in this lesson are evidence-based strategies that help promote young children’s social and emotional development and prevent and address challenging behaviors. But what does supporting children’s social and emotional development mean?
The term social emotional development refers to the Developing capacity of the child from birth through five years of age to Form close and secure adult and peer relationships; Experience, regulate, and express emotions in socially and culturally appropriate ways; and explore the environment and learn - All in the context of family, community, and culture.
Caregivers promote healthy Demo
development by working to support social emotional wellness in all young children, and make every effort to prevent the occurrence or escalation of social emotional problems in children at-risk, identifying and working to remediate problems that surface, and, when necessary, referring children and their families to appropriate services.The primary focus will be on developing relationships. One of our most important roles in supporting positive social emotional development with young children is to establish nurturing and trusting relationships. It is through these relationships that infants and toddlers learn about their world and their place in it. They learn that the world is safe and responsive to their needs. They learn to form satisfying relationships with others, to communicate, to face challenges, and to experience and regulate their emotions.
Since relationships are constantly adjusting to changes in development, we need to understand the course of social emotional development. Building positive relationships with both children and parents is essential for a child’s healthy development. Young children observe our relationships and what they observe shapes their expectations for how people treat each other. Relationships are established with each individual child and family and, therefore, look somewhat different with each.
Therefore as you explore this lesson on enhancing children’s social and emotional literacy, keep in mind the following key guidelines for implementing The Pyramid Model practices presented: